 |
 |
- Search
| Genomics Inform > Volume 19(4); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) facilitated the discovery of countless disease-associated variants. However, GWASs have mostly been conducted in European ancestry samples. Recent studies have reported that these European-based association results may reduce disease prediction accuracy when applied in non-Europeans. Therefore, previously reported variants should be validated in non-European populations to establish reliable scientific evidence for precision medicine. In this study, we validated known associations with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and related metabolic traits in 125,850 samples from a Korean population genotyped by the Korea Biobank Array (KBA). At the end of December 2020, there were 8,823 variants associated with glycemic traits, lipids, liver enzymes, and T2D in the GWAS catalog. Considering the availability of imputed datasets in the KBA genome data, publicly available East Asian T2D summary statistics, and the linkage disequilibrium among the variants (r2 < 0.2), 2,900 independent variants were selected for further analysis. Among these, 1,837 variants (63.3%) were statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05). Most of the non-replicated variants (n = 1,063) showed insufficient statistical power and decreased minor allele frequencies compared with the replicated variants. Moreover, most of known variants showed <10% genetic heritability. These results could provide valuable scientific evidence for future study designs, the current power of GWASs, and future applications in precision medicine in the Korean population.
Common diseases are a result of the complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors [1]. To date, several genetic studies have been conducted to identify diseases associated genetic variants and have used this gained knowledge as a clinical tool for disease prediction and prevention [2]. For the last decade, genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have been used as an efficient research tool for revealing numerous genetic variants associated with various diseases and traits [3]. Indeed, there were about 290K variants recorded in the NHGRI-EBI GWAS catalog [4].
Despite its great success, most GWASs have been conducted in European ancestry samples, and this Eurocentric bias may produce a significant reduction in disease prediction accuracy for non-Europeans [5,6]. This discrepancy might be caused by a difference in allele frequency distribution across populations and population-specific genetic effects [7,8]. Therefore, numerous studies have been conducted to validate previously reported diseases associated loci [9-12]. Here, we aimed to validate known associations with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and related metabolic traits in a large-scale East Asian population comprising of 125,850 Korean samples. Subsequently, this could establish reliable scientific evidence for disease prediction based on known T2D related associations in the Korean population.
The genetic components of complex diseases and traits were estimated as 30-70% based on family-based studies and statistical estimation using genome data. However, estimated heritability using validated loci showed only limited heritability, implying that there are more hidden genetic components to be revealed [13,14]. Since genetic variants are rapidly accumulating, it is valuable information to observe the current estimated genetic heritability status from known genetic variants. Therefore, we also estimated the genetic heritability from previously known variants associated with T2D and related quantitative traits.
Since 2001, the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) has recruited 211,725 participants from three population-based cohorts including the KoGES_Ansan and Ansung study, the KoGES_Health EXAminee (HEXA) study, and the KoGES_CardioVascular disease Associations Study (CAVAS) [15]. The details of these studies have been described elsewhere [15]. All participants were aged between 40 and 69 years and provided written informed consent. Thousands of variables from these participants, including epidemiological surveys, physical examinations, and laboratory tests, were examined. This study was approved by the institutional review board at the Korea National Institute of Health, Republic of Korea.
Glycemic traits, liver enzymes, lipid traits, and T2D were considered T2D-related traits. Glycemic traits were fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). Liver enzymes included alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Lipid traits included high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC). LDL was calculated using the Friedewald’s formula [16]. Participants taking medication or undergoing therapy likely influencing the traits were excluded from further analysis. All quantitative traits were transformed to follow an approximate normal distribution by inverse-variance or z-score normalization on residuals after regressing out age, gender, and recruitment area. TG was calculated using the log scale prior to transformation.
In this study, quality controlled genotypes of 125,850 samples genotyped by the Korea Biobank Array (KBA) were used. The KBA was optimized for genome studies in the Korean population comprising of approximately 830K variants [17]. The detailed genotyping and quality control processes have been reported previously [12,17]. In brief, genotypes were called by batches containing about 3,000 to 8,000 samples considering the recruitment area. Chromosomal position was based on hg19. Samples were excluded based on the following criteria: gender discrepancy, low call rate (<97%), excessive heterozygosity, 2nd-degree related samples using KING v2 [18], outliers of principle component analysis by using FlashPCA [19]. Following quality control, low-quality variants were excluded if they had a high missing rate (> 5%), Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium failure (p < 10-6), and low minor allele frequency (MAF) (< 1%). As a result, 125,850 samples were used for further analysis.
T2D-related variants were retrieved from a GWAS catalog database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/) [4]. To avoid possible false-positive studies with <1,000 samples were excluded for further analysis. As of December 31, 2020, there were 8,823 variants associated with glycemic traits, lipid traits, liver enzymes, and T2D listed in the GWAS catalog. Chromosomal positions of the variants from GWAS catalog were based on hg38. Thus, to match the chromosomal positions with the association results, LiftOver from UCSC genome browser was used to convert hg38 positions to hg19 [20]. Using the p-value of the cataloged variants and linkage disequilibrium (LD) information from the 1,000 Genomes project phase 3 East Asians or Europeans [21], two different clumping analysis was conducted to obtain independent variants for East Asians or Europeans (if it was available in the KBA imputed genotype data). For clumping analysis, plink was used with options including --clump-p1 1 --clump-p2 1 --clump-r2 0.l --clump-kb 500. Two sets of independently associated variants for East Asians or Europeans were then merged. Subsequently, 2,900 variants were selected as independent variants and used for further analysis.
The 8,823 variants associated with T2D related traits were imputed if they were not available in the KBA genotype data. KBA genotype data was phased using Eagle v2.3 [22] and imputed using Impute v4 (https://jmarchini.org/software/) [23] with a merged reference panel of 2,504 samples of 1,000 Genomes project phase 3 and 397 Korean whole genome sequencing data [17]. Linear regression analysis using transformed traits was performed using EPACTS v3.4.6 (http://genome.sph.umich.edu/wiki/EPACTS). T2D association results were assessed from publicly available summary statistics of previously conducted East Asian meta-analysis study [8]. R statistics program (version 4.0.5; https://www.r-project.org) was used to visualize the results. For lipids and T2D, we used LD score regression (LDSC) from bigsnpr R package to estimate genetic heritability of each trait using all variants matched with HapMap phase 3 within ±500 kb window of the independent variants [24,25]. For the other traits, heritability was estimated as the sum of estimated heritability for each variant using the effect size of the variant and variance of the associated trait. LDSC could not reliably calculate the correlation matrix of relatively small number of loci.
At the end of 2020, there were 8,823 variants associated with T2D-related traits including glycemic traits (FPG and HbA1c), lipids (HDL, LDL, TG, and TC), liver enzymes (AST, ALT, and GGT), and T2D in the GWAS catalog database. Because various studies have reported index variants closely located to each other, only independent variants with a high imputation quality score (≥0.8) were selected for further analysis by the clumping method, considering a linkage disequilibrium of r2 < 0.2 either in East Asian or European based on 1,000 genomes project data. Subsequently, 2,900 independent variants were identified and used in the association analysis. The overall analysis scheme is summarized in Fig. 1.
T2D-related metabolic traits, and the association results of the T2D variants were retrieved from a publicly available summary statistics of the DIAMANTE East Asians association study [8]. Overall, 1,837 variants (63.3%) were statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) (Table 1, Supplementary Table 1). The replication rate was the lowest for TG (51.9%) and the highest for HbA1c (84.5%).
The failure of replication in the Korean population could be due to insufficient statistical power and differences in genetic architectures. To study the possible reasons for this failure, we analyzed the statistical power and effect size distribution by MAF for the unvalidated variants (n = 1,063). The estimated statistical power with alpha of 0.05 is summarized in Table 2. Most of variants associated with T2D-related traits presented with insufficient statistical power, ranging from 0.36 for HbA1c to 0.68 for TG. However, 83 of 183 unvalidated T2D variants (45.3%) presented with enough statistical power (>80%), implicating a possible difference in genetic architecture across populations. Effect sizes by MAF of 1,063 non-replicated variants (n = 1,063) were plotted by each trait (Fig. 2, Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2). As expected, the effect size increased as MAF decreased. The effect sizes of non-replicated variants were closed to zero. Non-replicated variants were populated at a lower MAF than replicated variants, especially for glycemic traits and T2D.
To observe the current status of estimated genetic heritability from known genetic variants, genetic heritability was estimated using the effect sizes from known genetic variants (Table 3). The estimated heritability was the lowest for AST and ALT (1.32%) and the highest for TG (20.37%). However, estimated heritability was <10% for most traits implying that further analysis is needed to identify the hidden genetic components of T2D related traits.
In this study, associations of 2,900 known T2D related variants were validated in the 125,870 Korean samples. From these known variants, 1,837 (63.3%) were replicated, however, 1,063 variants were not replicated due to insufficient statistical power and difference in genetic architecture across populations. Most non-replicated variants showed insufficient statistical power (<0.8) and a relatively lower MAF than the replicated variants. Additionally, we estimated the current status of genetic heritability using the known variants. The genetic heritability from known loci was mostly less than 10% implying that there is a great portion of missing heritability for T2D-related variants. These results could provide valuable scientific evidence for future study design, the current power of GWAS, and future applications to precision medicine in the Korean population.
Despite these valuable findings of the current study, there were a few limitations and careful interpretation is required. First, given the insufficient statistical power from a limited number of sample size compared to that in previous studies conducted in Europeans [5-7], an association study with a larger sample size is warranted to achieve sufficient statistical power to investigate known associations. Second, we used the threshold as p ≤ 0.05. However, multiple testing considering number of independent variants is more reliable to avoid the inflation of false-positives. Third, independent variants were selected to avoid missing targets of previous reports based on linkage disequilibrium patterns from both East Asian and European populations. Therefore, high non-replicability might be caused by the inclusion of index variants from previous studies conducted in European populations. Finally, heritability was estimated using LDSC with all variants within the known loci or the sum of estimated heritability of independent variants. Some of traits with relatively small number of loci were unable to estimate the heritability using LDSC. Therefore, further study is warranted to estimate an accurate heritability accounting for genetic architecture within the loci.
Most of the non-replicated variants showed relatively less frequency compared to the replicated variants. To validate these variants in the Korean population, an immense sample size (up to millions) is required to obtain sufficient statistical power based on the estimated statistical power of non-replicated variants in this study. Insufficient statistical power from less frequent variants is a common problem in single ancestry studies [26,27]. Therefore, a trans-ethnic meta-analysis would be an adequate approach to identify hidden variants.
Notes
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by intramural grants from the National Institute of Health, Republic of Korea (2019-NI-097-02). Genotype data were provided by the Collaborative Genome Program for Fostering New Post-Genome Industry (3000-3031b).
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data can be found with this article online at http://www.genominfo.org.
Supplementary Table 1.
Replication results of known type 2 diabetes related variantsa
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of analysis flow. GWAS, genome-wide association study; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; T2D, type 2 diabetes; MAF, minor allele frequency; LD, linkage disequilibrium.
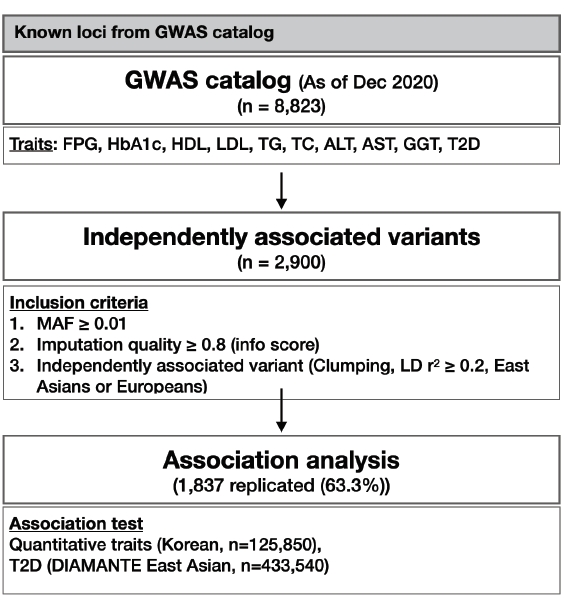
Fig. 2.
Effect sizes and minor allele frequency of variants associated with glycemic traits and type 2 diabetes. The X-axis represents the minor allele frequency of the variants. The Y-axis represents the absolute scale of effect sizes of variants. Each circle indicates a variant. Variants were colored in blue if they were replicated in this study (p ≤ 0.05) and colored in red otherwise (p > 0.05). (A) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG). (B) Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). (C) Type 2 diabetes (T2D).
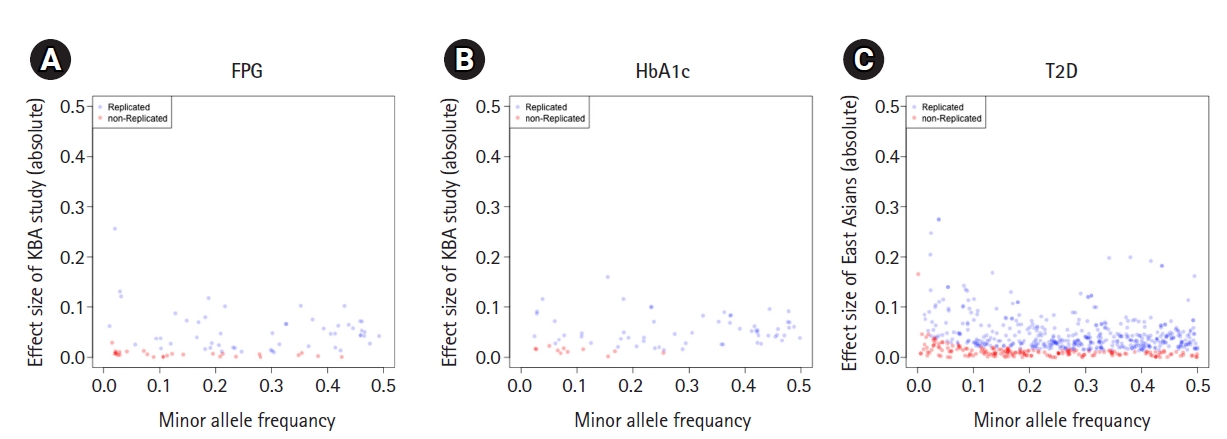
Table 1.
Summary of replication results
Table 2.
Estimated statistical power of non-replicated variants
Table 3.
Estimated genetic heritability of known variants
References
1. Claussnitzer M, Cho JH, Collins R, Cox NJ, Dermitzakis ET, Hurles ME, et al. A brief history of human disease genetics. Nature 2020;577:179–189.



2. Flannick J, Florez JC. Type 2 diabetes: genetic data sharing to advance complex disease research. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17:535–549.


3. Visscher PM, Wray NR, Zhang Q, Sklar P, McCarthy MI, Brown MA, et al. 10 Years of GWAS discovery: biology, function, and translation. Am J Hum Genet 2017;101:5–22.



4. Buniello A, MacArthur JA, Cerezo M, Harris LW, Hayhurst J, Malangone C, et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog of published genome-wide association studies, targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res 2019;47:D1005–D1012.


5. Sirugo G, Williams SM, Tishkoff SA. The missing diversity in human genetic studies. Cell 2019;177:26–31.



6. Martin AR, Kanai M, Kamatani Y, Okada Y, Neale BM, Daly MJ. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat Genet 2019;51:584–591.



7. Mahajan A, Taliun D, Thurner M, Robertson NR, Torres JM, Rayner NW, et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat Genet 2018;50:1505–1513.



8. Spracklen CN, Horikoshi M, Kim YJ, Lin K, Bragg F, Moon S, et al. Identification of type 2 diabetes loci in 433,540 East Asian individuals. Nature 2020;582:240–245.


9. Peprah E, Xu H, Tekola-Ayele F, Royal CD. Genome-wide association studies in Africans and African Americans: expanding the framework of the genomics of human traits and disease. Public Health Genomics 2015;18:40–51.


10. Gan W, Walters RG, Holmes MV, Bragg F, Millwood IY, Banasik K, et al. Evaluation of type 2 diabetes genetic risk variants in Chinese adults: findings from 93,000 individuals from the China Kadoorie Biobank. Diabetologia 2016;59:1446–1457.



11. Almawi WY, Nemr R, Keleshian SH, Echtay A, Saldanha FL, AlDoseri FA, et al. A replication study of 19 GWAS-validated type 2 diabetes at-risk variants in the Lebanese population. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2013;102:117–122.


12. Choi JY, Jang HM, Han S, Hwang MY, Kim BJ, Kim YJ. Recapitulation of previously reported associations for type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits in the 126K East Asians. Genomics Inform 2019;17:e48.



13. Almgren P, Lehtovirta M, Isomaa B, Sarelin L, Taskinen MR, Lyssenko V, et al. Heritability and familiality of type 2 diabetes and related quantitative traits in the Botnia Study. Diabetologia 2011;54:2811–2819.


14. Hou K, Burch KS, Majumdar A, Shi H, Mancuso N, Wu Y, et al. Accurate estimation of SNP-heritability from biobank-scale data irrespective of genetic architecture. Nat Genet 2019;51:1244–1251.



15. Kim Y, Han BG, Ko GE, KoGES group. Cohort profile: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:e20.


16. Johnson R, McNutt P, MacMahon S, Robson R. Use of the Friedewald formula to estimate LDL-cholesterol in patients with chronic renal failure on dialysis. Clin Chem 1997;43:2183–2184.


17. Moon S, Kim YJ, Han S, Hwang MY, Shin DM, Park MY, et al. The Korea Biobank Array: design and identification of coding variants associated with blood biochemical traits. Sci Rep 2019;9:1382.



18. Manichaikul A, Mychaleckyj JC, Rich SS, Daly K, Sale M, Chen WM. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2010;26:2867–2873.



19. Abraham G, Qiu Y, Inouye M. FlashPCA2: principal component analysis of Biobank-scale genotype datasets. Bioinformatics 2017;33:2776–2778.


20. Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM, et al. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002;12:996–1006.



21. 1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015;526:68–74.


22. Loh PR, Palamara PF, Price AL. Fast and accurate long-range phasing in a UK Biobank cohort. Nat Genet 2016;48:811–816.



23. Bycroft C, Freeman C, Petkova D, Band G, Elliott LT, Sharp K, et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018;562:203–209.



24. Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh PR, Finucane HK, Ripke S, Yang J, Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2015;47:291–295.



- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 4 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 4,008 View
- 143 Download







