 |
 |
- Search
| Genomics Inform > Volume 16(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Hybrid capture-based targeted sequencing is being used increasingly for genomic variant profiling in tumor patients. Unique molecular index (UMI) technology has recently been developed and helps to increase the accuracy of variant calling by minimizing polymerase chain reaction biases and sequencing errors. However, UMI-adopted targeted sequencing data analysis is slightly different from the methods for other types of omics data, and its pipeline for variant calling is still being optimized in various study groups for their own purposes. Due to this provincial usage of tools, our group built an analysis pipeline for global application to many studies of targeted sequencing generated with different methods. First, we generated hybrid capture-based data using genomic DNA extracted from tumor tissues of colorectal cancer patients. Sequencing libraries were prepared and pooled together, and an 8-plexed capture library was processed to the enrichment step before 150-bp paired-end sequencing with Illumina HiSeq series. For the analysis, we evaluated several published tools. We focused mainly on the compatibility of the input and output of each tool. Finally, our laboratory built an analysis pipeline specialized for UMI-adopted data. Through this pipeline, we were able to estimate even on-target rates and filtered consensus reads for more accurate variant calling. These results suggest the potential of our analysis pipeline in the precise examination of the quality and efficiency of conducted experiments.
The development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has brought remarkable growth in our understanding of human genome variants through comprehensive characterization. On top of that, various efforts have been made to find associations of these understandings with diseases, including cancers [1].
Particularly, detecting various mutations, including somatic mutations, is essential to comprehend the cancer genome [2]. However, this is one of the most challenging parts in studying cancer, because somatic mutations are sporadic among healthy cells [3], and therefore, variants with low allelic fractions are hard to track down [4]. Fortunately, targeted sequencing has been a great support to overcome these difficulties. Compared to whole-genome sequencing, targeted sequencing has several advantages in many aspects: high coverage data could be generated at a more reasonable price [5]; low-frequency variants could be detected with this ultra-deep sequencing [6]; and different types of mutations, such as single-nucleotide variants, short indels (insertion and deletions), structure variations, and copy number alterations, can be examined via targeted sequencing [7]. Therefore, many laboratories in both academia and the medical industry are making efforts to develop their own gene panels with various sizes.
However, the next predicament is the analysis of the targeted sequencing data, since the variants revealed in the data are hard to discriminate from false-positive errors. In detail, innate sequencing errors and early cycle polymerase chain reaction (PCR) biases during library amplification or target enrichment could be considered super or rare mutations during the variant calling process. To overcome this erroneous algorithm, unique molecular index (UMI) technology was recently developed [8]. UMIs, as 8–9-bp random oligonucleotides, barcode a single DNA molecule and index replicates generated from the same DNA templates during PCR amplification. Several proof-of-concept studies have proven the error correction mechanism of the UMI [6, 9–13], and they revealed that PCR biases and sequencing errors were compensated during consensus sequence extraction from reads with the same UMI tags [6]. Nevertheless, analyzing data with UMI is still a tedious task [8]. In other words, some UMI-analyzing and variant calling tools have limitations in their broad application to the data generated from different hybrid capture platforms or other types of sequencing data, such as single-cell sequencing. In addition, most files from each tool are not compatible with the tools in different pipelines. For example, a recently developed analysis tool, named smCounter2, is a variant caller and an analysis pipeline tool package for targeted sequencing data with UMIs. Purportedly, this tool is specialized to call low-frequency variants. However, the usage of smCounter2 is restricted only to the data generated by the QIAGEN QIAseq DNA target enrichment kit [6].
In this study, to build a versatile analysis pipeline to apply to various types of hybrid capture-based targeted sequencing, our laboratory evaluated various types of analysis tools, like Fulcrum genomics (fgbio, https://github.com/fulcrum-genomics/fgbio), Picard (http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard), and the Genome Analysis Tool Kit (GATK) [14]. We put our effort into optimizing the pipeline so as to not make discrepancies between the files and enable easier interpretation of the results. Furthermore, we show an example of how targeted sequencing experiments can be investigated for their quality from the analysis and how we could take points from the results analysis as feedback for the experiment.
Tumor tissues were dissected from 6 different colorectal cancer patients. Tumor samples were labeled from 1T to 7T, and sample 4T was omitted. NA24385 of the HapMap project and AccuRef Quan-Plex NGS Reference Standard Genomic DNA (cat# ARF-1001G-1; AccuRef, Milpitas, CA, USA) were used as positive controls.
For hybrid capture, all coding sequences of 46 genes and non-coding sequences of some of those genes were targeted. Pre-designed and customized probe sets were manufactured by Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT, Coralville, IA, USA).
To analyze UMI-adopted targeted sequencing data, we generated targeted sequencing libraries. During library generation, UMI sequences were integrated, along with the P5 sequencing adapter. Eight libraries were pooled together into one 1.7-mL microtube, and this 8-plex pooled library was then hybridized using IDT xGen LockDown pre-designed/custom probes. Targeted sequencing data of hybrid-capture library were generated using HiSeq series by 150-bp paired-end sequencing.
Using BclToFastq, the .bcl file was processed and divided into fastq files of read 1 (R1), read 2 (R2), and UMI. To generated unmapped bam files, R1.fastq and R2.fastq files were processed using FastqToBam (Fulcrum Genomics/fgbio, v0.7.0) (Fig. 1). Unmapped.bam file was then sorted using SortSam (Picard) to sort files compatible with downstream tools. UMI information was annotated via AnnotateBamWithUmis (fgbio). To use MergeBamAlignment (Picard) to generate UMI-annotated mapped bam files, SamToFastq (Picard) generated fastq files containing UMI information. Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA-mem, v0.1.17) aligned reads to the hg38 reference genome [15]. The unmapped bam files (output of Tool#3) and the aligned bam file (the output of BWA-mem) were merged via MergeBamAlignment (Picard). Mapped.bam file was then grouped by GroupReadsByUmi (fgbio) according to its RX-tagged UMI sequence. UMI family information was then used for grouping and calling consensus reads via CallMolecularConsensusReads (fgbio). FilterConsensusReads (fgbio) filters consensus reads to make bam files suitable for further variant calling. As CallMolecularConsensusReads and FilterConsensusReads generated unmapped bam files, converting bam files to fastq files, the mapping and merging steps were repeated for the variant calling in the following step. The overall pipeline is shown in Fig. 1.
UmiAwareMarkDuplicateWithMateCigar (Picard) counted duplicates among the raw reads to estimate duplicate rates. As this tool is still under development, we recommend a regular check with the developers on further validation. To calculate on-target rates (%), CollectHsMetrics (Picard) is used to generate HsMetrics. By expanding 100 bp of chromosome coordinates (start/end site) in target.bed, on-target %, including flanking regions, was calculated using the same tool. To calculate the read coverage, the following equation was used: Coverage = Read length(bp) × The number of reads/Genome size (bp). According to the manufacturer, the genome size refers to the target size of the probes.
First, total read counts were counted by either Picard tools or fgbio tools. An 8-plexed hybrid capture library generated 100 Gbp data, and approximately 15 Gbp data were generated from each sample. Considering the fact that the target genome size is 0.3 Mbp, the read coverages were calculated as 50,000× to 70,000×, as shown in Table 1. As on-target rate (%) represents how much the probes attach to the target genomic regions and as calculating on-target rates (%) refers to the efficiency of experiments, we examined the on-target rate (%). We were able to get 37% on-target rate, average (Table 1, Fig. 2). On-target rates were slightly increased when target regions were expanded to flanking regions (+100 bp). In addition, each sample showed a similar on-target %, and this may suggest that the hybridization step of targeted sequencing was processed with an even amount of each library.
Before removing sequence duplicates, we estimated duplicate read counts via UmiAwareMarkDuplicateWithMateCigar (Picard). We could measure duplicate rates of >70% of the reads (Fig. 3). Considering the fact that the percent duplicate increases as the sequencing coverage rises [16], an average 73% of duplicates indicates that the targeting efficiency of the probes was high in high-coverage sequencing. In addition, as we were aware that an excess number of PCR cycles during target enrichment brings severe biases [17], we assumed that the number of PCR cycles during enrichment was moderate. Although duplicate reads were not discarded in further steps, by checking duplicate rates, we confirmed that the number of PCR cycles during library preparation and target enrichment was adequate. In addition, we were able to verify the ability to examine the efficiency of our experiments through data analysis.
We then estimated the number of consensus reads to be ready for more accurate variant calling. Through this filtering, we were able to get the consensus coverage down to one-sixth of the raw coverage (Fig. 4). According to the filtering methods, the consensus sequences of each read from different UMI families were called for scanning variants. In addition, by calling and filtering consensus reads, the probability of errors was considered, according to the algorithm of the tool. Furthermore, the reads containing Ns or the reads with low confidence were filtered out for highly confident variant calling.
In this study, we built an analysis pipeline for targeted sequencing data generated based on the hybrid-capture method. As UMI-adopted targeted sequencing data are notorious for their novelty and complexity, we mainly focused on finding tools and optimizing methods for the analysis.
Our data show an on-target rate of 37%, and there is little variation among samples. This may suggest that almost equal amounts of libraries of each sample were used for hybridization. However, because 37% is relevantly low for hybridization efficiency, the estimation of the on-target rates shows that still there is room for improvement.
The reason why on-target rate is important is that by estimating on-target rates and further upgrades of protocols, the quality of targeted hybrid-capture sequencing could be improved. In detail, protocol modifications during hybridization steps could possibly bring about an increase of on-target rates. For example, a slightly excessive amount of input DNA or target probes can increase the off-target effects during hybridization. Furthermore, inconsistent temperature or slightly higher/lower temperature than the proper temperature could bring about larger off-target effects than expected.
With respect to the pipeline, when using CallMolecular ConsensusReads, insertion and deletion errors are not considered in the consensus model. Therefore, realignment steps using other methods, such as IndelRealigner (GATK, v4.0.2.1), should be integrated for better and more precise analysis for identification of short indels. Furthermore, even though we optimized the tools and customized python codes for analyzing UMI data, there are still many tools that could be used in one analysis pipeline. We are still trying to minimize irrelevant steps to simplify the process.
In summary, we have built an analysis pipeline specialized for UMI-adopted hybrid-capture-based data. Given the fact that the precision medicine era has been coming lately and that targeted sequencing and UMI technology help to comprehensively understand the genomewide status of cancer patients, this report suggests that the quality of the experiment can be examined precisely and efficiently by this pipeline, and our laboratory sees its positive potential in being widely used for studies in various clinical fields.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science & ICT (grant number: NRF-2017M3A9A7050614).
Fig. 1
Analysis pipeline. Tools and methods used in different file generation (fastq to input files for variant calling) are shown in the flow chart.

Fig. 2
Grouped histogram of on-target rate (%). On-target rate was expressed using the stacked histogram. The x-axis shows 6 tumor samples and one positive control. The upper part of each bar shows on-target % when the target region is enlarged with additional 50-bp flanking parts on both sides of each region.
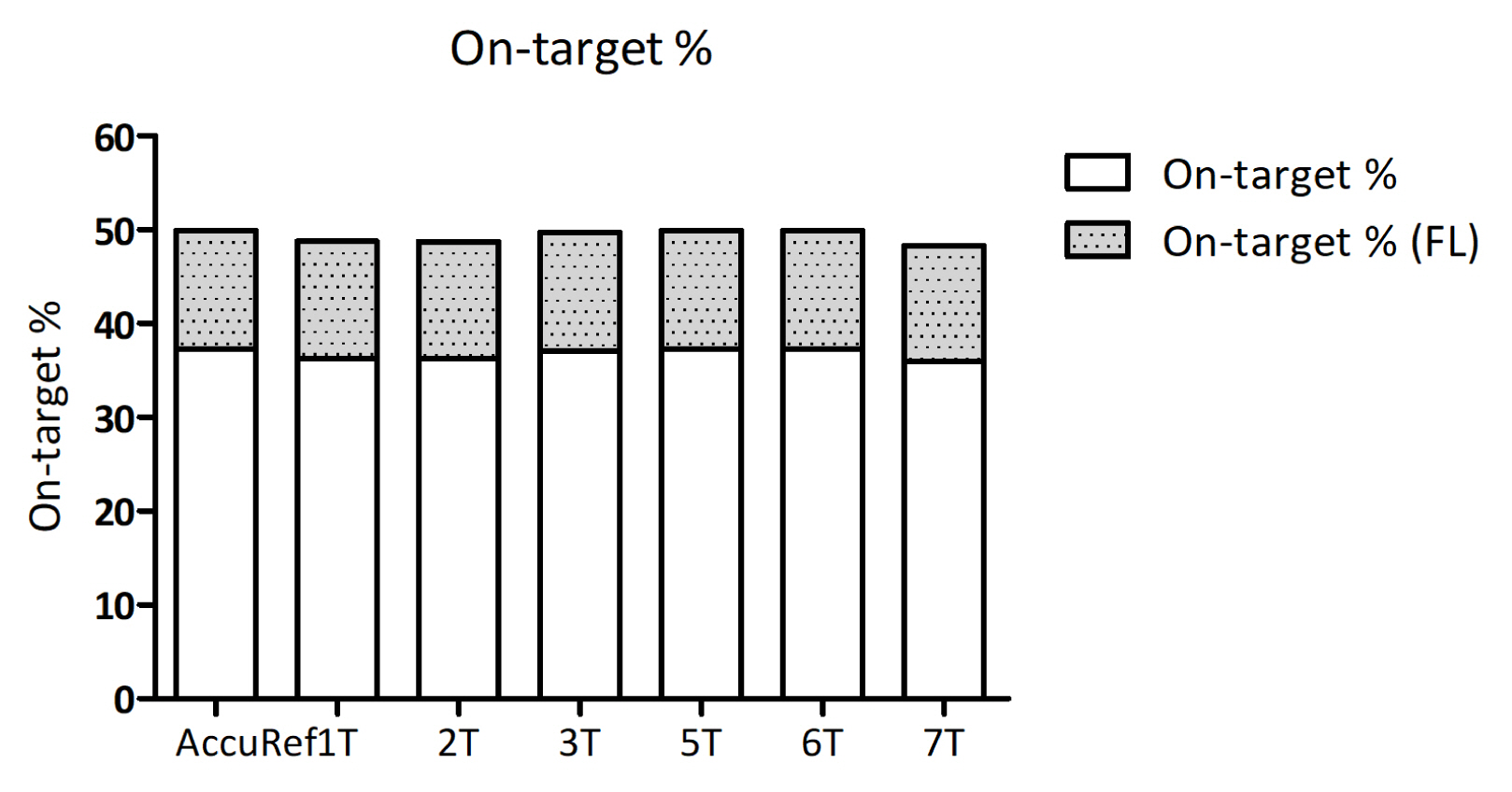
Fig. 3
Duplicate rate. Duplicate read ratio of each sample. Two positive controls are shown in the first two samples. The average duplicate rate is 0.73.
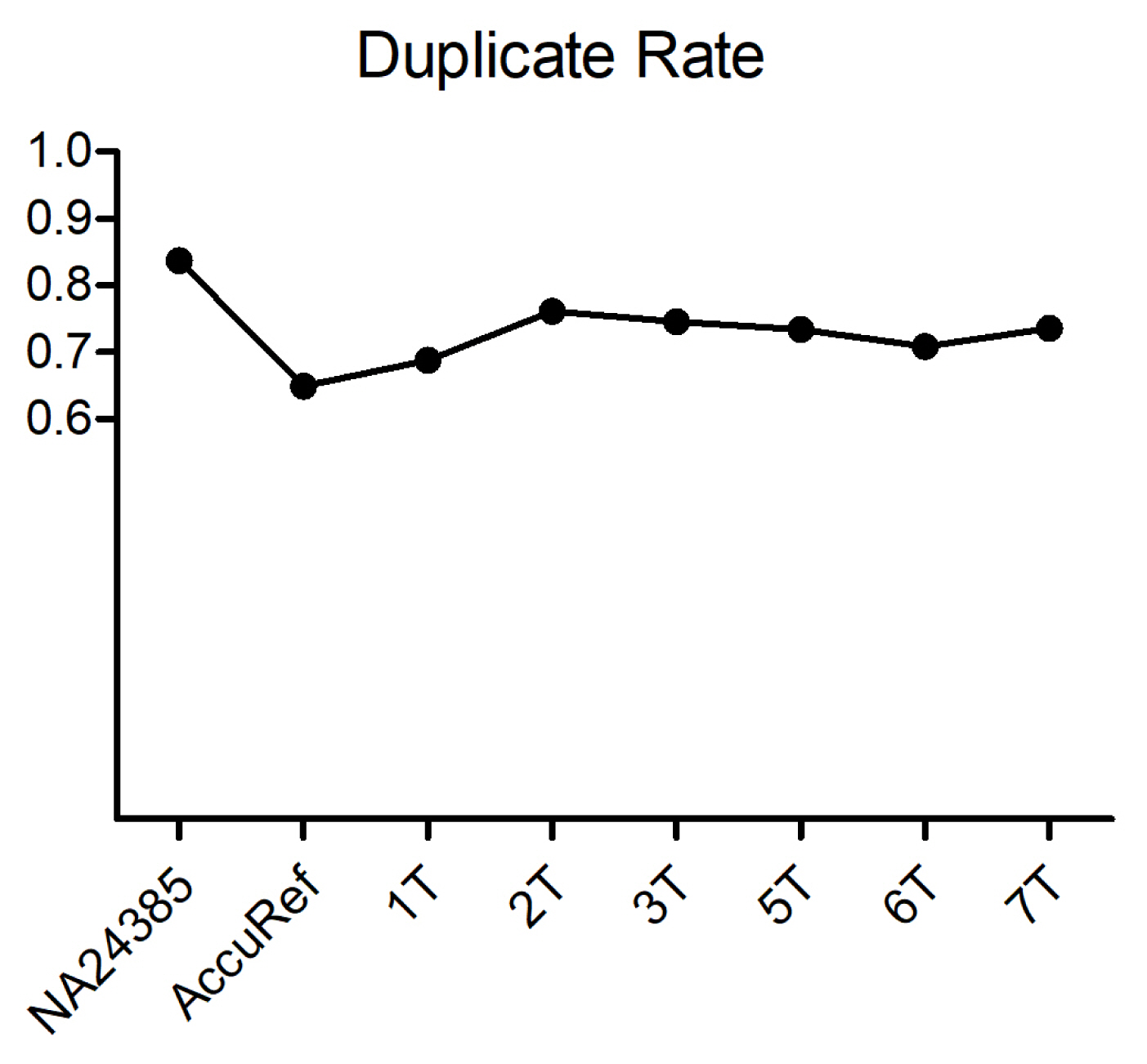
Fig. 4
Comparison of sequencing coverage from raw reads to filtered reads. The read coverage calculated from the read counts are shown with bar plots.

Table 1
Read counts and on-target rates (%)
Total raw reads and calculated coverage of raw data are shown in the first and second columns of the table, respectively. After examining on-target (%) with or without flanking regions, on-target coverage values were calculated in the last two columns. NA24385 and AccuRef were used as positive control samples.
References
1. 1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, et al. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010;467:1061–1073.



2. Cibulskis K, Lawrence MS, Carter SL, Sivachenko A, Jaffe D, Sougnez C, et al. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nat Biotechnol 2013;31:213–219.




4. Milbury CA, Li J, Makrigiorgos GM. Ice-COLD-PCR enables rapid amplification and robust enrichment for low-abundance unknown DNA mutations. Nucleic Acids Res 2011;39:e2.



5. Samorodnitsky E, Datta J, Jewell BM, Hagopian R, Miya J, Wing MR, et al. Comparison of custom capture for targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. J Mol Diagn 2015;17:64–75.



6. Xu C, Gu X, Padmanabhan R, Wu Z, Peng Q, DiCarlo J, et al. smCounter2: an accurate low-frequency variant caller for targeted sequencing data with unique molecular identifiers. Bioinformatics 2018 Sep 6 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty790.


7. Jennings LJ, Arcila ME, Corless C, Kamel-Reid S, Lubin IM, Pfeifer J, et al. Guidelines for validation of next-generation sequencing- based oncology panels: a Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology and College of American Pathologists. J Mol Diagn 2017;19:341–365.


8. Smith T, Heger A, Sudbery I. UMI-tools: modeling sequencing errors in Unique Molecular Identifiers to improve quantification accuracy. Genome Res 2017;27:491–499.



9. Jabara CB, Jones CD, Roach J, Anderson JA, Swanstrom R. Accurate sampling and deep sequencing of the HIV-1 protease gene using a Primer ID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:20166–20171.



10. Kennedy SR, Schmitt MW, Fox EJ, Kohrn BF, Salk JJ, Ahn EH, et al. Detecting ultralow-frequency mutations by Duplex Sequencing. Nat Protoc 2014;9:2586–2606.




11. Kukita Y, Matoba R, Uchida J, Hamakawa T, Doki Y, Imamura F, et al. High-fidelity target sequencing of individual molecules identified using barcode sequences: de novo detection and absolute quantitation of mutations in plasma cell-free DNA from cancer patients. DNA Res 2015;22:269–277.




12. Newman AM, Lovejoy AF, Klass DM, Kurtz DM, Chabon JJ, Scherer F, et al. Integrated digital error suppression for improved detection of circulating tumor DNA. Nat Biotechnol 2016;34:547–555.




13. Peng Q, Vijaya Satya R, Lewis M, Randad P, Wang Y. Reducing amplification artifacts in high multiplex amplicon sequencing by using molecular barcodes. BMC Genomics 2015;16:589.



14. McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 2010;20:1297–1303.



15. Lu H, Yang S, Zhu H, Tong X, Xie F, Qin J, et al. Targeted next generation sequencing identified clinically actionable mutations in patients with esophageal sarcomatoid carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018;18:251.




16. Sandhu SK, Wood AM, Kelchner V, Rosefigura J, Lenhart J, Kurihara L, et al. Breaking the NGS noise barrier to accurately detect variants below 1% allele frequency. J Mol Diagn 2017;19:1000.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 4 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 7,444 View
- 235 Download
- Related articles in GNI







