 |
 |
- Search
| Genomics Inform > Volume 14(2); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular Apicomplexan parasite and a causative agent of toxoplasmosis in human. It causes encephalitis, uveitis, chorioretinitis, and congenital infection. T. gondii invades the host cell by forming a moving junction (MJ) complex. This complex formation is initiated by intermolecular interactions between the two secretory parasitic proteins—namely, apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1) and rhoptry neck protein 2 (RON2) and is critically essential for the host invasion process. By this study, we propose two potential leads, NSC95522 and NSC179676 that can efficiently target the AMA1 hydrophobic cleft, which is a hotspot for targeting MJ complex formation. The proposed leads are the result of an exhaustive conformational search-based virtual screen with multilevel precision scoring of the docking affinities. These two compounds surpassed all the precision levels of docking and also the stringent post docking and cumulative molecular dynamics evaluations. Moreover, the backbone flexibility of hotspot residues in the hydrophobic cleft, which has been previously reported to be essential for accommodative binding of RON2 to AMA1, was also highly perturbed by these compounds. Furthermore, binding free energy calculations of these two compounds also revealed a significant affinity to AMA1. Machine learning approaches also predicted these two compounds to possess more relevant activities. Hence, these two leads, NSC95522 and NSC179676, may prove to be potential inhibitors targeting AMA1-RON2 complex formation towards combating toxoplasmosis.
Toxoplasma gondii is an Apicomplexan intracellular parasite and is a causative agent of toxoplasmosis in human. It also plays a key role over a broad spectrum of clinical syndromes, like encephalitis, uveitis, chorioretinitis, and congenital infections [1]. It infects the host by various modes, such as intake of undercooked meat containing T. gondii cysts, consumption of contaminated water, and food defilement with feces from infected cats, and may also spread through blood transfusion [2,3]. The sexual reproduction of T. gondii occurs in domestic cats, which are considered a definite host [4]. The asexual reproduction of this parasite occurs in intermediate hosts—namely, humans, cattle, and birds [5]. The establishment of host-parasite interactions is crucial for parasite survival, as it depends on host nutritive resources. Apicomplexan parasites implement a unique host cell invasion mechanism, wherein they anchor the host cell by forming multimeric protein machinery, called a moving junction (MJ) complex [6]. This complex is formed by interprotein interactions established between two types of proteins-namely, rhoptry neck proteins 2/4/5/8 (RON 2, 4, 5, and 8) proteins secreted by rhoptry organelle of the parasite onto the host membrane and apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1), secreted by micronemes [7,8,9]. The molecular association of RON2 and AMA1 is essential for initiating the host invasion process.
The hydrophobic cleft region of AMA1 is documented to play a predominant role in facilitating the binding of RON2 to AMA1 and is also reinforced by recent crystallographic studies on AMA1-RON2 complex formation [10]. Moreover, this region is found to be highly conserved across the diverse family of AMA1 proteins and is surrounded by polymorphic flexible loops. These loops are speculated to preclude the host antibody response and has also been found to guard the conserved sites in AMA1 [11]. The hydrophobic cleft is found to span within domain I of AMA1 and forms a binding pocket that receives the critical loop region of RON2 due to its accommodative shape and charge complementarity. The hydrophobic cleft region of AMA1 includes 15 residues (Val142, Leu155, Ile161, Phe163, Ile171, Phe174, Leu179, Ile185, Phe197, Met203, Tyr230, Val231, Trp253, Trp353, and Trp354) [12]. Recent studies illustrate that RON2 displaces a loop in domain II of AMA1, thereby exposing its binding surface, enabling the RON2 loop to penetrate deep into the hydrophobic groove of AMA1 and hence forming a stable complex during host invasion [13]. A recent study also showed that an oligopeptide binds across the full length of the AMA1 hydrophobic cleft to prevent AMA1-RON2 complex formation and eventually blocks parasitic host invasion [14,15]. Hence, the hydrophobic cleft and its surrounding loops, which include the cysteine loop region and coil connector, have been proposed to be a critical hotspot to block AMA1-RON2 complex formation. To date, there is a paucity of data on small molecules targeting these interactions. Hence, in this study, the coordinates of the crystal structure complex depicting these interactions (Protein Data Bank [PDB] ID 2Y8T, AMA1 interacting with a surface-exposed region of RON2) [16] were subjected to an exhaustive, multilevel precision high-throughput virtual screen (HTVS) of ligands from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) database with 250,000 compounds to identify leads that potentially disrupt these interactions. We also implemented molecular dynamics (MD) simulation analysis to decipher the backbone rigidity changes of AMA1 hotspot residues, machine learning-based activity prediction, and binding free energy calculations for finalizing the potential lead compounds towards combating toxoplasmosis (Fig. 1) [17].
As an initial step, the crystal coordinates of AMA1 in complex with a surface-exposed region of RON2 (PDB ID: 2Y8T) was pre-processed using Protein Preparation Wizard of the Schrödinger (New York, NY, USA) suite towards optimizing the stereochemistry by assigning proper bond order, removing steric clashes, adding hydrogen atoms, fixing the disulfide bonds and missing residues and loops. Furthermore, optimization of the protein structure was also performed by adjusting the terminal chi rotation of asparagine, glutamine, and histidine residues. Optimal protonation states for histidine residues were also assigned, followed by the removal of unwanted hetero groups. Finally, energy minimization was performed with OPLS_2005 (Schrödinger) to obtain the optimal geometry.
The receptor grid for docking was generated by assigning the entire hydrophobic cleft region of AMA1 to which the RON2 binds, thereby performing an exhaustive cavity search towards achieving an optimal ligand binding pose. The residues spanning the RON2 binding cavity were noted from the Dimplot generated for the AMA1-RON2 complex [16]. The van der Waals radii for the receptor were assigned with a scaling factor of 1.0 and a partial cutoff of 0.25. The grid-assigned residues were Leu99, Val105, Leu109, Tyr110, Arg111, Val142, Phe143, Thr144, Glu145, Leu155, Asn162, Thr165, Gln169, Arg170, Ile171, Asn182, Asn184, Leu200, Thr201, Val202, Ala203, Met204, Tyr213, Tyr215, Tyr230, Ser232, Met233, Met236, Tyr241, Thr252, Trp253, Gln338, Phe339, and Gln361.
To expedite the virtual screening of ligands, the NCI ligand datasets (250,000 compounds) were screened for drug-likeness by implementing the Lipinski rule. The filtered molecules were optimized by the LigPrep module (Schrödinger) by fixing the ring isomers, stereoisomers, and tautomeric forms. The reactive functional groups were also removed, and the resultants were scaled for van der Waals radii with a scaling factor of 0.80 and a partial charge cutoff of 0.15. Finally, the compounds passing all these filters were energy-minimized with OPLS_2005 as the force field.
The in silico virtual screening and docking of optimized NCI compounds against AMA1 were performed using the Glide HTVS option of the Schrodinger suite 2012 (Schrödinger, LLC). As a first step, the entire RON2-interacting cavity was fixed as a grid box. The van der Waals radius scaling was set to 1.0 to allow free scaling to soften the non-polar regions of the receptor and the rest of the other atoms. Finally, the optimized small molecules were successively docked to AMA1, ensuring flexible sampling with no more than 300 atoms and 50 rotatable bonds. A total of 10 energetically favorable conformations were selected among the 1,000 generated poses per docking, and the best docked complexes were finalized, based on the Glide docking score. During the screening process, successive elimination of ligand hits was performed through three filtering modes using the Schrödinger suite: 100% of HTVS hits were passed to standard precision (SP), and 80% of the best hits from SP were passed to extra precision (XP) mode. The top 10 hits in XP, based on Glide score, were shortlisted for further validation [18].
The putative activities of the top 10 compounds were predicted using Prediction of Activity Spectra of Substances (PASS). It implements a machine learning-based algorithm called biological activity spectrum (with 95% accuracy), and it works by describing the intrinsic properties of the compounds and by comparing the structure of the new compound with the structure of well-known biologically active substances to check whether the new compound exhibits any of the specific functional effects [19]. Among the 10 shortlisted compounds, four showed significant activity relevant towards suppressing toxoplasmosis, along with a favorable Glide docking score. Hence, these four compounds were subjected to a rigorous validation process of calculating Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area (MMGBSA) score and by performing an MD simulation.
MMGBSA scoring was performed for the top 4 complexes, so as to calculate and identify binding free energies in an explicit-solvent exposed state by implementing the Prime module of the Schrodinger suite. A more negative MMBGSA score indicates stronger binding [20].
MD simulation for both apo and the docked complexes was performed using Desmond 3.6. The simulation was initiated using the OPLS_2005 [21] force field with the system solvated using the simple point charge water model. The system was neutralized by adding 4 Na+ for apo and 6 Na+ counter ions for complexes at a concentration of 4.751 mM. Further, this system was energy-minimized with OPLS_2005. The SHAKE algorithm was applied to restrain the geometry of water molecules and bond lengths and bond angles of heavy atoms [22]. Periodic boundary conditions were applied to stimulate a continuous system [23] and the particle mesh Ewald method for long-range electrostatics [24]. Further, the system was equilibrated with NPT ensemble by setting the temperature and pressure parameters to 300 K and 1.0 bar, respectively. The Berendsen coupling algorithm was chosen for temperature-pressure coupling [25]. Further, the equilibrated system, with a total of 74,931 atoms, was exposed to a simulation period of 5,000 ps with a time step of 2 fs, and trajectories were recorded after every 1.0 ps. The root mean square deviation (RMSD) was calculated for the backbone atoms and were graphically analyzed on a time point scale [26,27]. Similarly, root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) for each residue was also calculated to compare the major conformational changes in the residues between apo and holo forms [28]. The radius of gyration (Rg) was also calculated to infer the compactness of the protein-ligand complex against the apo form [29]. Two-dimensional intermolecular interaction plots depicting the complex stability throughout the MD run were also generated to infer the stability of the protein-ligand complex formation.
Three different stages of the docking and scoring processes were used for this study, beginning with HTVS, followed by SP and final scoring with XP. AMA1 protein was sequentially docked with compounds from the NCI database using Schrodinger Glide. Initially, HTVS was performed, wherein 146,670 compounds were scored as hits, based on Glide score. Subsequently, these compounds were passed to SP mode, which yielded 1,466 compounds. Finally, within the SP resultant hits, 147 compounds were scored as potential hits in XP mode. Further, these compounds were ranked in accordance with the XP docking score, and the top 10 ranking compounds proceeded to further analysis. These top 10 compounds were filtered further, based on Glide docking score, significant intermolecular interactions, and PASS prediction. Interestingly, all 10 of these compounds were found to occupy the hotspot region, which includes the hydrophobic cleft and cysteine loop region of AMA1, despite reference-guided docking procedures (Table 1).
Scoring functions play a major role in the docking process for identifying plausible ligand binding poses and also for ranking the binding affinity. Among the top 10 compounds, NSC95522, NSC88253, NSC13604, and NSC179676 (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. 1) were found to be highly significant in collective terms of XP Glide score, PASS prediction, formation of intermolecular H-bonds, and π-cation interactions with the critical hydrophobic cleft residues, as well as in the cysteine loop region. NSC95522 showed a Glide score of -10.564 kcal/mol and formed π-cation interactions with Tyr110, Tyr213, and Tyr215, stabilized by 3 hydrogen bonds formed with Tyr230, Ser232, and Tyr215 (Supplementary Fig. 1A). Tyr230 is a vital residue in the hydrophobic cleft, as it is the central tyrosine of the apical groove and is mandatory for RON2 binding and also in the formation of a contiguous surface, which is critical for MJ assembly [30]. Ser232 is also documented in Plasmodium falciparum as a key hotspot residue, as it occupies the hydrophobic cleft-spanning region [31]. Tyr213 and Tyr215 are also crucial, as these residues are key facilitators of conformational changes in AMA1 DII loop displacement towards exposing a clear pocket to which Pro1309 of RON2 docks to the triad of tyrosine residues (Tyr110/142, Tyr213/234, and Tyr215/236) during AMA1-RON2 interactions [32]. PASS predicted this compound to be an ophthalmic drug and thus might also be found to be effective in treating adverse ocular-related effects due to toxoplasmosis.
NSC88253 was bound to the hydrophobic cleft of AMA1 with a XP Glide score of -10.392 kcal/mol, forming almost similar interactions to that of the AMA1-NSC95522 complex with 3 hydrogen bonds: 2 with the backbone of Tyr230 and Ser232 and 1 with the side chain of Tyr215. The π-cation interactions with Tyr110 and Tyr213 were also synonymously stabilized by hydrogen bonds formed by residues Tyr230, Tyr215, and Ser232 (Supplementary Fig. 1B). Tyr110 is a coil connector and is documented to play an important role in the displacement of the DII loop of AMA1, which helps in the binding of RON2 [32]. PASS predicted this compound to be an ophthalmic drug with anticataract and corneal wound healing-stimulating activities, thus suggesting it to be an efficient inhibitor targeting ocular toxoplasmosis.
NSC13604 also showed interactions at the hydrophobic cleft of AMA1, with a XP Glide score of -10.016 kcal/mol. The docked complex showed 2 hydrogen bonds with the peptide backbone of Met204, which occupies the cysteine loop region. It also formed π-cation interactions with Tyr213 and Tyr110, stabilized by the hydrogen bonds formed with Met204 (Supplementary Fig. 1D). Met204 is a key residue for AMA1 targeting, as it is present in the cysteine loop region, which is also a critical substructure for AMA1-RON2 complex formation. As per previous studies, disruption of the cysteine loop is found to exhibit inefficiency in domain-II loop displacement [17]. PASS predicted this compound to be antiprotozoal and may prove it to be efficient in targeting toxoplasmosis and also other apicomplexans.
NSC179676 showed interactions with the hydrophobic cleft, with an XP score of -9.893 kcal/mol. It formed a single hydrogen bond with the backbone Ser232, which is a critical residue, as discussed earlier. It also formed π-cation interactions with Tyr213 and Tyr110 (Supplementary Fig. 1I). PASS predicted this molecule to be antiprotozoal with corneal wound healing-stimulating activities. These four compounds exhibited significant features in terms of XP score, key molecular interactions, and relevant predicted activity in comparison to rest of the compounds. Hence, these compounds in complex with AMA1 were further validated for stability of complex formation by implementing MD simulation.
MD trajectory analyses were performed for apo and also for the 4 shortlisted complexes. The backbone RMSD deviation of the apo form of AMA1 was 1.6 Å, which has started to equilibrate and converge after 3,000 ps with a mean of 1.432 Å and a standard deviation (SD) of 0.178 Å. The receptor RMSD for all 4 holo forms showed convergence after the time frame ranging between ~3,000 and 4,000 ps, with a maximum mean value of 1.65 Å and SD of 0.27 Å (Fig. 2A). Hence, it does not mandate an extended production run. In the case of holo forms, the ligand_RMSD for NSC95522, NSC13604, and NSC179676 was less than 2.5 Å (acceptable range of 1–3 Å) [33], while NSC88253 showed 3.6 Å of deviation, inferring complex instability (Fig. 2B–F).
The RMSF graph inferred NSC95522 and NSC179676 to exhibit the least fluctuation of <1 Å at the critical hotspot residues (Tyr230, Tyr213, Tyr15, and Tyr110) in comparison to the apo form, indicating a gain of backbone rigidity. As discussed earlier, flexibility of these residues is crucial for homing RON2. However, the other two compounds did not show this impact (Fig. 3A and 3B). Moreover, the Rg for both apo and all 4 holo forms was found to be within an admissible deviation of <1 Å. NSC95522 and NSC179676 showed the lowest Rg deviation of 0.44 Å and 0.53 Å, while the apo form showed 0.57 Å; thus, this reinforces that these two compounds confer backbone rigidity and compactness, which strongly preclude RON2 binding (Fig. 3C). Secondary structure element (SSE) perturbations were also analyzed in a similar way as discussed above. This inferred no major dynamism in the SSE during the entire production run; it also corroborated with the fewest changes observed in the intra-molecular hydrogen bonds formed for the apo and all other 4 holo forms (Fig. 3D). For all four of these compounds, the stability of protein-ligand contacts during the production run was analyzed and visualized as a 2D interaction map (Fig. 4A–D). This inferred π-cation interactions to be unanimously stable for all four compounds. Recent studies propose that ligands exhibiting π-cation interactions with Phe, Tyr, and Trp of the receptor highly influence the conformational stability of the proteins, as they are strong non-covalent electrostatic interactions [34,35]. A holistic and stringent comparative analysis was performed over the 4 holo forms against the apo form, which strongly reinforces that AMA1-NSC95522 and AMA1-NSC179676 are stable complexes. Moreover, both these compounds exhibit prominent π-cation interactions with the proven hotspot residues Tyr213, Tyr230, Tyr110, and Tyr215 of AMA1 for ~80% of the entire production run, implying that these compounds are potential blockers of conformational changes of AMA1, which facilitates the binding of RON2 [35]. The MMGBSA scores of the AMA1-NSC95522 and AMA1-NSC179676 complexes were found to be -79 kcal/mol and -59 kcal/mol respectively, also ensuring significant binding and stable complex formation [20].
In conclusion, NSC95522 and NSC179676 shall be considered the most potential leads, with both showing significant binding free energies with strong intermolecular interactions to hydrophobic cleft residues. Moreover, these compounds were also found to limit the torsion angle of the AMA1 tilt of 90°, while the other two compounds showed a wide range of deviation (~90° to 180°). Hence, all of these inferences strongly suggest that NSC95522 and NSC179676, with antiprotozoal and ophthalmic activity, shall prove to be highly efficient leads for targeting AMA1-RON2 interactions (Fig. 4E), thereby combating toxoplasmosis. However, further experimental validation is required to study the efficacy of these molecules.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, under RGYI scheme [BT/PR6476/GBD/27/496/2013, 05/09/2013].
Supplementary materials
Supplementary data including one figure can be found with this article online at http://www.genominfo.org/src/sm/gni-14-53-s001.pdf.
Supplementary Fig. 1
(A–J) The docked complex showing ligand binding interactions with hydrophobic cleft residues of apical membrane antigen 1.
References
1. Holland GN. Ocular toxoplasmosis: a global reassessment. Part I: epidemiology and course of disease. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;136:973–988. PMID: 14644206.


2. Thirumudi I, Vetrivel U, Mahalakshmi B, K LT, Hn M. Insights on drug targeting of Toxoplasma gondii host invasion proteins: a review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2015;8:52–57.
3. Tenter AM, Heckeroth AR, Weiss LM. Toxoplasma gondii: from animals to humans. Int J Parasitol 2000;30:1217–1258. PMID: 11113252.



4. Kim K, Weiss LM. Toxoplasma gondii: the model apicomplexan. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:423–432. PMID: 15003501.



5. Hehl AB, Basso WU, Lippuner C, Ramakrishnan C, Okoniewski M, Walker RA, et al. Asexual expansion of Toxoplasma gondii merozoites is distinct from tachyzoites and entails expression of non-overlapping gene families to attach, invade, and replicate within feline enterocytes. BMC Genomics 2015;16:66. PMID: 25757795.



6. Aikawa M, Miller LH, Johnson J, Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites: a moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol 1978;77:72–82. PMID: 96121.



7. Alexander DL, Mital J, Ward GE, Bradley P, Boothroyd JC. Identification of the moving junction complex of Toxoplasma gondii: a collaboration between distinct secretory organelles. PLoS Pathog 2005;1:e17. PMID: 16244709.



8. Besteiro S, Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M. The moving junction of apicomplexan parasites: a key structure for invasion. Cell Microbiol 2011;13:797–805. PMID: 21535344.


9. Straub KW, Peng ED, Hajagos BE, Tyler JS, Bradley PJ. The moving junction protein RON8 facilitates firm attachment and host cell invasion in Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog 2011;7:e1002007. PMID: 21423671.



10. Besteiro S, Michelin A, Poncet J, Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M. Export of a Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry neck protein complex at the host cell membrane to form the moving junction during invasion. PLoS Pathog 2009;5:e1000309. PMID: 19247437.



11. Lamarque M, Besteiro S, Papoin J, Roques M, Vulliez-Le Normand B, Morlon-Guyot J, et al. The RON2-AMA1 interaction is a critical step in moving junction-dependent invasion by apicomplexan parasites. PLoS Pathog 2011;7:e1001276. PMID: 21347343.



12. Henderson KA, Streltsov VA, Coley AM, Dolezal O, Hudson PJ, Batchelor AH, et al. Structure of an IgNAR-AMA1 complex: targeting a conserved hydrophobic cleft broadens malarial strain recognition. Structure 2007;15:1452–1466. PMID: 17997971.


13. Crawford J, Tonkin ML, Grujic O, Boulanger MJ. Structural characterization of apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1) from Toxoplasma gondii. J Biol Chem 2010;285:15644–15652. PMID: 20304917.



14. Harvey KL, Yap A, Gilson PR, Cowman AF, Crabb BS. Insights and controversies into the role of the key apicomplexan invasion ligand, apical membrane antigen 1. Int J Parasitol 2014;44:853–857. PMID: 25157917.


15. Collins CR, Withers-Martinez C, Hackett F, Blackman MJ. An inhibitory antibody blocks interactions between components of the malarial invasion machinery. PLoS Pathog 2009;5:e1000273. PMID: 19165323.



16. Richard D, MacRaild CA, Riglar DT, Chan JA, Foley M, Baum J, et al. Interaction between Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1 and the rhoptry neck protein complex defines a key step in the erythrocyte invasion process of malaria parasites. J Biol Chem 2010;285:14815–14822. PMID: 20228060.



17. Tonkin ML, Roques M, Lamarque MH, Pugnière M, Douguet D, Crawford J, et al. Host cell invasion by apicomplexan parasites: insights from the co-structure of AMA1 with a RON2 peptide. Science 2011;333:463–467. PMID: 21778402.


18. Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, et al. Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 2006;49:6177–6196. PMID: 17034125.


19. Lagunin A, Stepanchikova A, Filimonov D, Poroikov V. PASS: prediction of activity spectra for biologically active substances. Bioinformatics 2000;16:747–748. PMID: 11099264.


20. Genheden S, Ryde U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2015;10:449–461. PMID: 25835573.



21. DuBay KH, Hall ML, Hughes TF, Wu C, Reichman DR, Friesner RA. Accurate force field development for modeling conjugated polymers. J Chem Theory Comput 2012;8:4556–4569. PMID: 26605615.


22. Barth E, Kuczera K, Leimkuhler B, Skeel RD. Algorithms for constrained molecular dynamics. J Comput Chem 1995;16:1192–1209.

23. Bulatov VV, Rhee M, Cai W. Periodic boundary conditions for dislocation dynamics simulations in three dimensions. MRS Proc 2000;653:Z1–Z3.

24. Harvey MJ, De Fabritiis G. An implementation of the smooth particle mesh Ewald method on GPU hardware. J Chem Theory Comput 2009;5:2371–2377. PMID: 26616618.


25. Berendsen HJ, Postma JP, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 1984;81:3684–3690.

26. Damm KL, Carlson HA. Gaussian-weighted RMSD superposition of proteins: a structural comparison for flexible proteins and predicted protein structures. Biophys J 2006;90:4558–4573. PMID: 16565070.



27. Maiorov VN, Crippen GM. Significance of root-mean-square deviation in comparing three-dimensional structures of globular proteins. J Mol Biol 1994;235:625–634. PMID: 8289285.


28. Fuglebakk E, Echave J, Reuter N. Measuring and comparing structural fluctuation patterns in large protein datasets. Bioinformatics 2012;28:2431–2440. PMID: 22796957.


29. Lobanov MY, Bogatyreva NS, Galzitskaya OV. Radius of gyration as an indicator of protein structure compactness. Mol Biol 2008;42:623–628.

30. Srinivasan P, Beatty WL, Diouf A, Herrera R, Ambroggio X, Moch JK, et al. Binding of Plasmodium merozoite proteins RON2 and AMA1 triggers commitment to invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:13275–13280. PMID: 21788485.



31. Alam A. Bioinformatic identification of peptidomimetic-based inhibitors against Plasmodium falciparum antigen AMA1. Malar Res Treat 2014;2014:642391. PMID: 25580351.




32. Tonkin ML, Crawford J, Lebrun ML, Boulanger MJ. Babesia divergens and Neospora caninum apical membrane antigen 1 structures reveal selectivity and plasticity in apicomplexan parasite host cell invasion. Protein Sci 2013;22:114–127. PMID: 23169033.



33. Carugo O. How root-mean-square distance (r.m.s.d.) values depend on the resolution of protein structures that are compared. J Appl Cryst 2003;36:125–128.


34. Mahadevi AS, Sastry GN. Cation-π interaction: its role and relevance in chemistry, biology, and material science. Chem Rev 2013;113:2100–2138. PMID: 23145968.


35. Scrutton NS, Raine AR. Cation-π bonding and amino-aromatic interactions in the biomolecular recognition of substituted ammonium ligands. Biochem J 1996;319:1–8. PMID: 8870640.



Fig. 1
Schematic representation of methodology of performing an exhaustive search and stringent validations in identifying potential leads for combating toxoplasmosis. Multilevel precision: screens the National Cancer Institute (NCI) ligands based on Glide docking score. Molecular Docking: identifies the favorable interactions formed with the key residues. Pass: helps in discovering additional effects of the top compounds that might favor in suppressing the broad spectrum of toxoplasmosis effects. Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area (MMGBSA): calculates the free energy binding. Molecular dynamics: evaluates the backbone stability, fluctuation, and compactness of the complex. HTVS, high-throughput virtual screen; PASS, Prediction of Activity Spectra of Substances; RMSD, root mean square deviation; RMSF, root mean square fluctuation; SP, standard precision; XP, extra precision.
Fig. 2
(A) Root mean square deviation (RMSD) of apo against holo forms within 2.5 Å. (B, D, E) Protein-ligand RMSD converged within 1~3 Å. (C) RMSD of NSC88253 exhibited instability with deviation of 3.6 Å. (F) The RMSD score of the apo and holo forms.

Fig. 3
(A) The root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) fluctuations of apo against holo forms. (B) RMSF<1 Å within hotspot residues. (C) Radius of gyration depicting compactness of the apo and holo forms. (D) Intramolecular H-bonds showing secondary structure element stability.
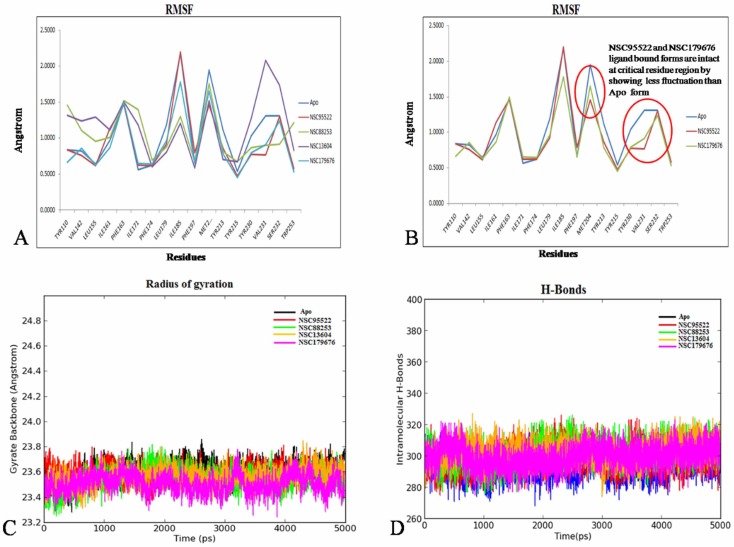
Fig. 4
(A) Interaction stability diagram for NSC95522 showing a stable π-cation interaction with Tyr213 and H-bond interaction with Ser232. (B) NSC88253 did not form any stable interactions during the production run. (C) NSC13604 exhibited a prominent π-cation interaction with Tyr110. (D) NSC179676 displaced a stable π-cation interaction with Tyr230 and Tyr110 and water-mediated H-bond with Ser232. (E) Three-dimensional representation of ligands NSC95522 (green) and NSC179676 (magenta) interacting with the hotspot residue region (blue) of apical membrane antigen 1.

Table 1.
Docking molecular interactions of 10 best compounds with XP Glide score
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 9 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 7,887 View
- 75 Download
- Related articles in GNI





