 |
 |
- Search
| Genomics Inform > Volume 10(3); 2012 > Article |
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the leading causes of cancer deaths and can be caused by environmental factors as well as genetic factors. Therefore, we developed a prediction model of CRC using genetic risk scores (GRS) and evaluated the effects of conventional risk factors, including family history of CRC, in combination with GRS on the risk of CRC in Koreans. This study included 187 cases (men, 133; women, 54) and 976 controls (men, 554; women, 422). GRS were calculated with most significantly associated single-nucleotide polymorphism with CRC through a genomewide association study. The area under the curve (AUC) increased by 0.5% to 5.2% when either counted or weighted GRS was added to a prediction model consisting of age alone (AUC 0.687 for men, 0.598 for women) or age and family history of CRC (AUC 0.692 for men, 0.603 for women) for both men and women. Furthermore, the risk of CRC significantly increased for individuals with a family history of CRC in the highest quartile of GRS when compared to subjects without a family history of CRC in the lowest quartile of GRS (counted GRS odds ratio [OR], 47.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.9 to 471.8 for men; OR, 22.3; 95% CI, 1.4 to 344.2 for women) (weighted GRS OR, 35.9; 95% CI, 5.9 to 218.2 for men; OR, 18.1, 95% CI, 3.7 to 88.1 for women). Our findings suggest that in Koreans, especially in Korean men, GRS improve the prediction of CRC when considered in conjunction with age and family history of CRC.
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also called colon cancer or large bowel cancer, includes cancerous growths in the colon, rectum, and appendix [1]. With 655,000 deaths worldwide per year, it is the fourth most common form of cancer in the United States (US) and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the western world [1, 2]. In Korea, CRC is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers, and its incidence is now dramatically increasing with the westernization of lifestyles [3]. According to statistics for Korea, the incidence of CRC was 9.8 per 100,000 men and 10.4 per 100,000 women from 1999-2001 [4]. These incidence rates for CRC increased to 18.2 per 100,000 men and 13.7 per 100,000 women in 2003 [5].
Given the high incidence of CRC and its significant cost to society, the ability to accurately predict the possibility of developing the disease using identifiable risk factors may help both physicians and patients prevent its occurrence [6]. Numerous studies have identified risk factors related to CRC, such as age, sex, family history of CRC, smoking, physical activity, aspirin/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use, vegetable intake, body mass index (BMI), alcohol consumption, and hormone replacement therapy by women [7-10].
Recently, there have been a number of studies that developed a risk score or a prediction model of certain diseases, such as coronary heart disease (CHD) and cancers, using these identified risk factors [11, 12]. However, these risk scores or prediction models have excluded genetic risk factors. Genetic polymorphisms contributing to certain disease incidences, such as CHD, could be one type of emerging risk factor under investigation in studies generally focused on a priori selected candidate genes [13, 14]. Advances in genome technologies have made it possible to genotype and evaluate many single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) throughout the human genome to identify novel disease susceptibility genes [15].
A CRC prediction model has been developed in a previous study that estimates the probability of developing CRC, given a specific age, risk factor profile, and time period in white men and women aged 50 years and older [16]. However, genetic polymorphisms have not been included in the study. Another prediction model, developed among middle-aged Japanese men, included conventional risk factors without genetic risk factors [17]. A recent study developed a prediction of CHD risk, aggregating information from multiple SNPs into a single genetic risk score (GRS) and determined an improvement in the prediction of incident CHD in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study [18].
From recent studies, several SNPs that may play an important role in triggering CRC have been introduced by a genome-wide association study (GWAS) among whites, Japanese, and Chinese but not Koreans [19-22]. Moreover, prediction models that were developed recently were performed among whites and the Japanese population [16, 17]. Previous studies have shown that combining multiple loci with modest effects into a global GRS might improve the identification of persons who are at risk for common complex diseases [23-25]. Therefore, in this study, we intended to describe a GRS by aggregation of multiple SNPs contributing to CRC through a GWAS. Furthermore, we aimed to develop a prediction model consisting of conventional risk factors as well as a genetic risk factor, such as GRS, in Koreans in the Korean Cancer Prevention Study-II (KCPS-II).
The initial study population included 200,595 individuals, 20-77 years of age, who visited 16 health promotion centers nationwide from April 2004 to December 2007 in the KCPS-II. Of these, there were 325 confirmed cases of CRC [26], but 132 cases Ōēź55 years of CRC onset age were excluded to obtain early-onset CRC cases. For controls, they were recruited from the Korean Metabolic Syndrome Research Initiative study, a part of KCPS-II, in Seoul, initiated in December 2005. A total of 9,128 individuals were recruited in 2006, and an additional 17,569 individuals were recruited in 2007. Therefore, the total Seoul cohort included 26,697 volunteers. Volunteers from the first round had routine health examinations at the Health Promotion Center in university hospitals between January 2006 and December 2007. From this total, 1,004 individuals were genotyped using Affymetrix Genomewide Human SNP Array 5.0 (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA). However, 10 of 1,004 individuals were removed because of low genotyping call rates (<95%), and 4 individuals were shown to have biological relatives; so, one member of each pair was excluded. Eleven and 2 individuals were also excluded as a result of gender mismatches [27]. An additional 6 cases and 1 control were excluded due to missing anthropometric measurements (height, weight, BMI, waist circumstance [WC], and blood pressure [BP]) and self-reported questionnaire information (smoking status and alcohol consumption). A detailed description of the KCPS-II study design and methods of selection of controls in this study are published elsewhere [27]. Therefore, a total of 1,163 participants (men, 687; women, 476) were included in this study: 187 cases (men, 133; women, 54) and 976 controls (men, 554; women, 422). A written consent form was signed by all study participants, and the Institutional Review Board of Yonsei University approved the study protocol.
DNA samples were isolated from the peripheral blood of participants and genotyped using Affymetrix Genomewide Human SNP Array 5.0 (Affymetrix Inc.) at DNA Link Inc. (Seoul, Korea). Internal quality control (QC) measures were employed to ensure accuracy of the data. The QC call rate (dynamic model algorithm) was Ōēź95%, and heterozygosity of X chromosome markers identified the gender for each sample. Genotype calling was performed by Birdseed (v2) algorithm. Chromosome Y was not analyzed. A total of 1,163 individuals were genotyped via this platform in the analysis. PLINK (v1.07) was used to estimate identity by state (IBS) over all SNPs [28]. A default set of 426,019 SNPs was used for further analysis, as recommended by Affymetrix. In the quality assurance screening, we flagged SNPs with genotype call rates < 95%, minor allele frequencies < 0.01, and SNPs showing deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) at p < 0.0000001. The final set of acceptable markers included 312,506 autosomal SNPs. Accuracy of the genotyping was calculated by Bayesian robust linear modeling using the Mahalanobis distance (BRLMN) algorithm [29].
Serum, separated from peripheral venous blood, was obtained from each participant after a 12-h fast and then stored at -70Ōäā until analyzed. For anthropometric measurements, WC was measured on exposed waists midway between the lower rib and the iliac crest using a measuring tape. For difficult cases, WC was measured at 3 cm above the navel. Weight and height were measured while participants were wearing light clothing. BMI was calculated as weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2). Both systolic and diastolic BP was measured after a 15-min rest. In addition, each participant was interviewed using a structured questionnaire to collect information on smoking and alcohol consumption as well as demographic characteristics, such as age, gender, and family and past history of clinical diseases. Cigarette smoking was classified into never smokers, ex-smokers, and current smokers. Alcohol consumption was divided into nondrinkers and current drinkers. Regular physical activity was tracked as either "yes" or "no".
In the association of SNPs with CRC, the SNPs with p < 10-5 in Korean men were: rs17391002 (CXCL12), rs9549448 (SOX1), rs254833 (MYO10), rs2553614 (TMEM71), rs13153032 (NSUN2), rs2288073 (FLJ30851), rs9604214 (SOX1), rs9865670 (OPA1), rs17186320 (KIAA1009), rs1509497 (RFX8), rs235428 (PHF20L1), rs9845920 (OPA1), rs9846212 (OPA1), rs6763744 (OPA1), rs4128317 (ALK), rs7646304 (OPA1), rs17047306 (SPATA17), rs1490338 (SPATA17), rs902351 (SPATA17), and rs2543662 (ITSN2) (Supplementary Table 1). The SNPs with p < 10-5 in Korean women in the association between SNPs and CRC were: rs10083736 (GOT2), rs16987827 (DHX35), rs8046516 (GOT2), rs9926182 (GOT2), rs17523778 (FAM174B), rs4974411 (TPRA1), rs1834902 (H2AFY), rs16895308 (MAST4), rs8032832 (FAM174B), rs6901560 (PD6), rs11025480 (PRMT3), rs3814110 (BNC2), rs16895307 (MAST4), rs7089063 (MARCH8), rs16893688 (IBTK), rs6861487 (MAST4), rs9613463 (MN1), rs11242237 (H2AFY), rs11150094 (WWOX), and rs9625253 (MN1) (Supplementary Table 2). Each SNP in this study was assumed to be associated with risk according to an additive genetic model, which performs well, even when the true genetic model may not be known or may be incorrectly specified [30].
A GRS was calculated on the basis of reproducible tagging of SNP-associated loci reaching genomewide levels of significance. In this study, the GRS was calculated with the 3 SNPs in Korean men and 5 SNPs in Korean women showing the strongest association with CRC (p < 10-6). The GRS was created by two methods: a simple count method (count GRS) and a weighted method (weighted GRS) [31, 32]. Both methods anticipated each SNP to be independently associated with risk. We assumed an additive genetic model for each SNP, applying a linear weighting of 0, 1, or 2 to genotypes containing 0, 1, or 2 risk alleles, respectively. This model is known to perform well, even when the true genetic model is unknown or wrongly specified [30]. The count model assumes that each SNP in the panel contributes equally to the risk for CRC and was calculated by summing the values for each of the SNPs. The weighted GRS was calculated by multiplying each beta-coefficient by the number of corresponding risk alleles (0, 1, 2).
The principle outcome variables were prevalence (n = 165) and incidence rates (n = 22), based on national cancer registry and hospitalization records. Although Korea has a national cancer registry, reporting was not complete during the time of follow-up, and consequently, hospital admission files were used to identify first admission events for CRC. An incident of CRC was coded as occurring, based on either a positive report from the national cancer registry or upon hospital admission for a cancer diagnosis [33]. According to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), CRC was coded as C18-C20 [34].
All analyses were conducted using PLINK version 1.06 (Free Software Foundation, Inc., Boston, MA, USA) and SAS statistical software version 9.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). All statistical tests were two-sided, and statistical significance was determined as p < 0.05. To evaluate general characteristics of the study population, means and standard deviations (SD) were calculated, and frequency of cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical activity was determined. Paired t-tests were performed to indicate the differences between case participants and control participants for both men and women. A X2 goodness-of-fit test was used to assess whether SNPs were in HWE and to determine differences in genotype frequencies between CRC cases and controls. The GRS was categorized into quartiles. The CRC risk associated with genotype was estimated as s ORs and 95% confidence interval (CI), computed using logistic regression with an additive genetic model. We also used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and calculated the area under the curve (AUC; also known as the C statistic) to evaluate the discrimination power of the model. In addition, internal validity of each model was checked using bootstrap [35], while 10-fold crossvalidation was used for the external validity of each model (Supplementary Tables 3 and 4) [36].
Our analysis included 687 men (cases, 133; controls, 554) and 476 women (cases, 54; controls, 422), 20-77 years of age. The number of prevalent cases of CRC identified was 166. An additional 22 incident cases of CRC occurred during follow-up. Table 1 details the general characteristics of case participants and control participants at baseline. The mean age (SD) was 42.9 (┬▒ 8.7) years for the study population-43.5 (┬▒ 8.9) for men and 42.0 (┬▒ 8.4) for women, respectively. No significant differences were observed in BMI, WC, systolic BP, or diastolic BP among case participants and control participants for both men and women (p > 0.05); however, case participants were older and had a family history of CRC more than control participants in both men and women (p < 0.001).
Table 2 indicates the area under the ROC curves for models that included both conventional risk factors and a genetic risk factor, GRS, compared with the AUC for the model that included only conventional risk factors. In the prediction model of CRC, we included age and family history of CRC as conventional risk factors and counted GRS or weighted GRS as genetic risk factors. For both men and women, including the GRS in the model increased the AUC over that observed when the AUC was based on only age or age and family history of CRC. For men, the AUC (95% CI) was 0.729 (range, 0.682 to 0.767) for conventional risk factors plus counted GRS (p < 0.001) and 0.719 (range, 0.677 to 0.761) for conventional risk factors plus weighted GRS (p < 0.001). The AUC (95% CI) was 0.692 (range, 0.647 to 0.732) for conventional risk factors alone. The increase in the AUC for the model with counted GRS was 0.042 and 0.032 for the model with weighted GRS. For women, the AUC (95% CI) was 0.650 (range, 0.615 to 0.680) for conventional risk factors plus counted GRS (p < 0.001) and 0.646 (range, 0.612 to 0.674) for conventional risk factors plus weighted GRS (p < 0.001). The AUC (95% CI) was 0.603 (range, 0.569 to 0.637) for conventional risk factors alone. The increase in the AUC for the model with counted GRS was 0.052 and 0.048 for the model with weighted GRS.
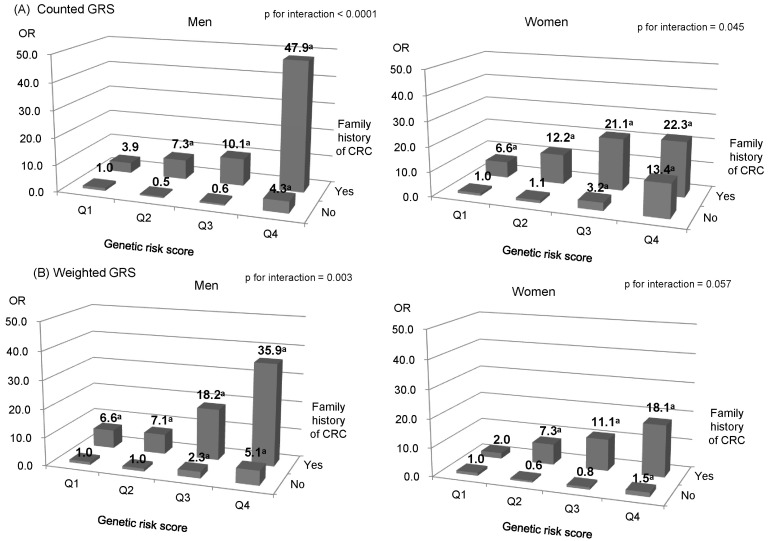
We further examined the association between GRS and CRC risk for both men and women in the KCPS-II, with stratification by family history of CRC (Fig. 1). The interaction between counted or weighted GRS and family history of CRC was significant in men, indicating a stronger genetic effect among participants with a positive family history of CRC than in those without it (p for interaction < 0.05) (ROC, 0.834 for counted GRS; ROC, 0.822 for weighted GRS). Women with a positive family history of CRC in the highest quartile of weighted GRS had an OR of 22.3 (95% CI, 1.4 to 344.2) and 18.1 (95% CI, 3.7 to 88.1) compared to those without a family history of CRC and counted or weighted GRS in the lowest quartile, respectively (ROC = 0.826 for counted GRS; ROC = 0.818 for weighted GRS). However, they were not statistically significant (p for interaction > 0.05). In addition, smoking, alcohol consumption, BMI, and WC did not interact significantly with GRS (data not shown).
This study evaluated the ability of the GRS, which aggregates information from multiple genetic variants, to improve the prediction of CRC risk beyond the prediction risk afforded using conventional risk factors. For both men and women, inclusion of counted GRS or weighted GRS increased the AUC by 0.5% to 4.2% beyond the AUC provided by conventional risk factors, such as age and family history of CRC. Men with a positive family history of CRC and GRS in the highest quartile were determined to have a statistically significant increased risk of CRC than those without a family history of CRC and GRS in the lowest quartile. However, women with a positive history of CRC and GRS in the highest quartile were determined to have an increased risk of CRC than those without a family history of CRC and GRS in the lowest quartile, but this result was not statistically significant.
CRC is a multifactorial disease involving a variety of elements, leading to the development of clinical manifestations [37]. This recognition had led to the development of risk assessment tools that attempt to synthesize the values of numerous variables into a single statement regarding the risk of developing cancer [38]. In this study, 20 SNPs were respectively genotyped in Korean men and women. Among these SNPs, 3 SNPs in Korean men and 5 SNPs in Korean women showing the strongest association with CRC were used for the calculation of GRS. The GRS was calculated using a linear weighting of 0, 1, or 2 for genotypes containing 0, 1, or 2 risk alleles, respectively. The weighted GRS was computed by multiplying each beta-coefficient by the number of corresponding risk alleles. However, when multiplying each beta-coefficient by the number of corresponding risk alleles, negative values of beta-coefficients may be obtained in some genotypes of the SNPs. Therefore, it may affect the OR values for CRC when compared to the OR values for CRC determined using counted GRS. Still, the calculation results of both counted GRS and weighted GRS were similar to each other.
Cornelis et al. [31] and Ripatti et al. [32] used methods similar to the GRS created for our study. Several other studies have reported different ways of calculating risk scores for the prediction of diseases [39-41]. Horne et al. [39] introduced a regression method for calculating risk scores that incorporated 3 genetic polymorphisms and other risk factors and found that the frequency of coronary heart disease was different at different regression score levels. Ortlepp et al. [40] concluded that multiple SNPs are better than single SNPs and that as many as 200 SNPs may be necessary for "reasonable" genetic discrimination. Aston et al. [41] suggested that a score based on 90 SNPs in 78 genes can predict the risk of breast cancer, but the identity of the SNPs and the algorithm for calculating the score remain proprietary. An alternative way to calculate GRS using machine approaches, such as support vector machines (SVMs), could be introduced, as SVMs have already been used to deal with many biological problems, such as DNA expression profiles [42]. Still, further studies are needed to use machine learning approaches, such as SVMs, for the calculation of GRS. To our knowledge, there have been no studies evaluating a GRS using SNPs contributing to CRC for the prediction of the disease in the Korean population.
The present study evaluated a prediction model using counted GRS or weighted GRS together with conventional risk factors, such as age and family history of CRC among Koreans. The risk of CRC is said to increase in individuals with a family history of CRC, in particular those >50 years of age [43, 44]. From a recent study, a CRC prediction model was developed with known major risk factors of age, BMI, alcohol consumption, smoking status, and physical activity level for middle-aged Japanese men [17]. Another recent study on the prediction model of CRC included an individual's age, sex, history of CRC, sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy, polyps, family history of CRC, smoking, physical activity, aspirin/NSAID use, vegetable intake, BMI, and hormone replacement in women [16]. In our study, the prediction model of CRC was comprised of conventional risk factors, such as age and family history of CRC, together with the GRS. As determined, inclusion of counted GRS or weighted GRS revealed improved estimates of CRC prediction beyond that provided by conventional risk factors, such as age and family history of CRC. For example, when counted GRS were added to the prediction model of CRC consisting of age and family history of CRC, the AUC increased by 4.2% in men and 5.2% in women, whereas the AUC increased by 3.2% in men and 4.8% in women when weighted GRS were added to the same model. Studies showing significant relationships of GRS in conjunction with coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and breast cancer have reported that considering the contribution of multiple SNPs may improve the predictive value of GRS for such diseases [18, 31, 45]. In other words, combining multiple loci with modest effects into a global GRS might improve identification of persons who are at risk for such diseases [23-25]. For example, in the ARIC study, the contribution of multiple SNPs into a single GRS was responsible for an improvement in the prediction of incident CHD [18]. In a study that used counted GRS or weighted GRS to determine the risk for type 2 diabetes in US men and women, individuals in the highest quintile of GRS had a significantly increased risk of type 2 diabetes compared to those in the lowest quintile; however, the addition of GRS increased the AUC by only 1%. In this instance, the GRS was determined to be useful when combined with the joint effects of BMI and counted GRS or family history of diabetes and counted GRS [30]. In our study, individuals in the highest quartile of GRS had increased risk of CRC compared to those in the lowest quartile of GRS for both men and women. In addition, in strata of family history of CRC and GRS, this increase was even higher in individuals with a family history of CRC in the highest quartile of GRS compared to those without a family history of CRC in the highest quartile of GRS in both men and women. Still, there were statistically significant interactions in men but not in women. In this study, the most commonly used conventional risk factors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, were also not included in the prediction model of CRC, as smoking, alcohol consumption, BMI, and WC did not significantly interact with the GRS. Therefore, further studies are needed to verify these results.
A family history of CRC is commonly used as a surrogate marker for determining genetic susceptibility to CRC and remains one of the strongest risk factors for the disease [10, 31, 46]. Approximately 25% of all CRC cases occur in individuals with a family history of the disease and no genetic disorders [47]. In addition, some retrospective studies have suggested that a history of CRC in a first-degree relative (a parent or sibling) elevates a person's lifetime risk of CRC from 1.8-fold to 8.0-fold [10, 47]. This family history risk factor may encompass both genetic and shared environmental components [31]. In our study, after controlling for age and GRS, the strong relationship between family history of CRC and risk of CRC persisted. These findings suggest that other risk loci remain to be discovered or that family history has a much larger shared environmental component than previously thought [31].
Our study was not without limitations. The cross-sectional design precluded the determination of causality, and a prevalent case bias may exist due to the higher number of prevalent cases (n = 165) of CRC included compared to the number of incident cases (n = 22). Combining prevalence and incidence cases could introduce survival biases. Still, the 5-year survival rate for CRC in Koreans was 71.3% in 2009 while that in Americans, Europeans, and Japanese was 65.0%, 56.2%, and 65.2%, respectively [43]. It could be said that Koreans have higher survival rates for CRC compared to other ethnic populations. Additionally, this study is also a case-cohort study. Blood samples of prevalent cases used in this study were from baseline, and incidence cases during the follow-up period, suggested as prevalent cases in this study, might have been missed, as other blood samples were not taken. Therefore, those prevalent cases at baseline might have become incident cases or mortality cases during the follow-up period. It is hard to say if this study was performed among survivors. Another limitation included a self-reported family history of CRC, thus precluding the definitive exclusion of potential misclassifications. The statistical power of the current study might be too low, as genotyping was performed separately for men and women. In addition, performing multiple tests separately in both men and women may increase error rates. Although CRC affects men and women equally, gender differences in CRC may exist. For example, regarding colorectal polyps and tumors, men had a greater risk of polyps (OR, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.41 to 1.64) and tumors (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.22 to 1.68) than women. In addition, women had greater number of purely right-sided polyps and tumor development [48]. Therefore, detection of genetic effects separately in men and women may be needed. In addition, age differences in case and control participants may also increase error rates, as control participants may become CRC patients when they reach the case age. This study also involved the lack of validation and replication of the current study results. Therefore, it is hard to say that there may have been a true association between GRS and CRC in Korean men and women. However, bootstrapping and 10-fold cross validation were used for internal and external validity of this current study. Furthermore, although sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy history was the strongest risk factor in the previous study, this current study did not include it as one of the conventional risk factors of CRC. Cases included in this study were also relatively small. This study also excluded cases Ōēź 55 years of CRC onset age to obtain early-onset CRC cases. Therefore, estimate effects of cases Ōēź 55 years of CRC onset age were hard to be seen in this study. Finally, most SNPs found to be associated with CRC among the study population were not similar to those SNPs found in relation to CRC among other populations. It also could be due to differences in ethnic population and the ages of case participants included in this study (cases < 55 years). Nevertheless, this relatively large-scale study demonstrated the effectiveness of the prediction model of CRC using the GRS consisting of only SNPs that associated significantly with CRC and evaluated the effects on the risk for CRC in combination with conventional risk factors, such as family history of CRC, with the GRS. Moreover, the present study included the Korean population, whereas previous studies involving CRC prediction models using conventional risk factors or the relationship of genetic risk factors to CRC were limited to white and Japanese populations [17, 20-22].
In conclusion, our findings suggest that the prediction model of CRC revealed improved prediction estimates when age, family history of CRC, and the GRS in the Korean population were included. Furthermore, when compared to those in the lowest quartile of GRS in the presence or absence of a family history of CRC, the risk of CRC was found to be significantly increased in individuals with a family history of CRC in the highest quartile of GRS. However, it was statistically significant in men but not in women. Findings in this current study might provide a small piece of evidence in prediction of CRC for reducing its prevalence and incidence rates. The prediction model developed in this study needs to be validated or replicated in an independent population. Therefore, further studies are needed to be applied to the general population.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an extramural grant from the Seoul R&BD program, Republic of Korea (10526); a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control; Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (0920330); the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2011-0029348); and a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control; Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (1220180).
Supplementary materials
Supplemetary data including four tables can be found with this article online at http://www.genominfo.org/src/sm/gni-10-175-s001.pdf.
References
1. Cancer. 2011. Accessed 2012 Jul 5. Geneva: World Health Organization, Available from: http:www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en.
2. Cancer of the Colon and Rectum. 2011. Accessed 2012 Jul 5. Bethesda: National Cancer Institute, Available from: http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/wyntk/colon-and-rectal.
3. Lee YS, Choi HB, Lee IK, Kim TG, Oh ST. Association between interleukin-4R and TGF-beta1 gene polymorphisms and the risk of colorectal cancer in a Korean population. Colorectal Dis 2010;12:1208ŌĆō1212. PMID: 19863607.


4. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. The National Cancer Registry. 2003. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
5. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). 2007. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
6. Freedman AN, Seminara D, Gail MH, Hartge P, Colditz GA, Ballard-Barbash R, et al. Cancer risk prediction models: a workshop on development, evaluation, and application. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:715ŌĆō723. PMID: 15900041.


7. Park Y, Freedman AN, Gail MH, Pee D, Hollenbeck A, Schatzkin A, et al. Validation of a colorectal cancer risk prediction model among white patients age 50 years and older. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:694ŌĆō698. PMID: 19114700.



8. Otani T, Iwasaki M, Inoue M. Shoichiro Tsugane for the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study Group. Body mass index, body height, and subsequent risk of colorectal cancer in middle-aged and elderly Japanese men and women: Japan public health center-based prospective study. Cancer Causes Control 2005;16:839ŌĆō850. PMID: 16132794.


9. Harriss DJ, Atkinson G, Batterham A, George K, Cable NT, Reilly T, et al. Lifestyle factors and colorectal cancer risk (2): a systematic review and meta-analysis of associations with leisure-time physical activity. Colorectal Dis 2009;11:689ŌĆō701. PMID: 19207713.


10. Fuchs CS, Giovannucci EL, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Speizer FE, Willett WC. A prospective study of family history and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1669ŌĆō1674. PMID: 7969357.


11. Tamimi RM, Rosner B, Colditz GA. Evaluation of a breast cancer risk prediction model expanded to include category of prior benign breast disease lesion. Cancer 2010;116:4944ŌĆō4953. PMID: 20645399.



12. Kivim├żki M, Nyberg ST, Batty GD, Shipley MJ, Ferrie JE, Virtanen M, et al. Does adding information on job strain improve risk prediction for coronary heart disease beyond the standard Framingham risk score? The Whitehall II study. Int J Epidemiol 2011;40:1577ŌĆō1584. PMID: 21558169.



13. Cauchi S, El Achhab Y, Choquet H, Dina C, Krempler F, Weitgasser R, et al. TCF7L2 is reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes in various ethnic groups: a global meta-analysis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85:777ŌĆō782. PMID: 17476472.


14. Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C, Shen L, Serre D, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007;445:881ŌĆō885. PMID: 17293876.


15. Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Jonsdottir T, Walters GB, et al. A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007;39:770ŌĆō775. PMID: 17460697.


16. Freedman AN, Slattery ML, Ballard-Barbash R, Willis G, Cann BJ, Pee D, et al. Colorectal cancer risk prediction tool for white men and women without known susceptibility. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:686ŌĆō693. PMID: 19114701.



17. Ma E, Sasazuki S, Iwasaki M, Sawada N, Inoue M, et al. Shoichiro Tsugane. 10-Year risk of colorectal cancer: development and validation of a prediction model in middle-aged Japanese men. Cancer Epidemiol 2010;34:534ŌĆō541. PMID: 20554262.


18. Morrison AC, Bare LA, Chambless LE, Ellis SG, Malloy M, Kane JP, et al. Prediction of coronary heart disease risk using a genetic risk score: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am J Epidemiol 2007;166:28ŌĆō35. PMID: 17443022.


19. Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, et al. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer--analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med 2000;343:78ŌĆō85. PMID: 10891514.


20. Zanke BW, Greenwood CM, Rangrej J, Kustra R, Tenesa A, Farrington SM, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 8q24. Nat Genet 2007;39:989ŌĆō994. PMID: 17618283.


21. Xiong F, Wu C, Bi X, Yu D, Huang L, Xu J, et al. Risk of genome-wide association study-identified genetic variants for colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010;19:1855ŌĆō1861. PMID: 20530476.


22. Tenesa A, Farrington SM, Prendergast JG, Porteous ME, Walker M, Haq N, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on 11q23 and replicates risk loci at 8q24 and 18q21. Nat Genet 2008;40:631ŌĆō637. PMID: 18372901.



23. Meigs JB, Shrader P, Sullivan LM, McAteer JB, Fox CS, Dupuis J, et al. Genotype score in addition to common risk factors for prediction of type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2208ŌĆō2219. PMID: 19020323.



24. Weedon MN, McCarthy MI, Hitman G, Walker M, Groves CJ, Zeggini E, et al. Combining information from common type 2 diabetes risk polymorphisms improves disease prediction. PLoS Med 2006;3:e374. PMID: 17020404.



25. Wray NR, Goddard ME, Visscher PM. Prediction of individual genetic risk to disease from genome-wide association studies. Genome Res 2007;17:1520ŌĆō1528. PMID: 17785532.



26. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. The National Cancer Registry. 2007. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
27. Jee SH, Sull JW, Lee JE, Shin C, Park J, Kimm H, et al. Adiponectin concentrations: a genome-wide association study. Am J Hum Genet 2010;87:545ŌĆō552. PMID: 20887962.



28. Purcell S, Neale K, Todd-Brown L, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007;81:559ŌĆō575. PMID: 17701901.



29. Rabbee N, Speed TP. A genotype calling algorithm for affymetrix SNP arrays. Bioinformatics 2006;22:7ŌĆō12. PMID: 16267090.


30. Balding DJ. A tutorial on statistical methods for population association studies. Nat Rev Genet 2006;7:781ŌĆō791. PMID: 16983374.


31. Cornelis MC, Qi L, Zhang C, Kraft P, Manson J, Cai T, et al. Joint effects of common genetic variants on the risk for type 2 diabetes in U.S. men and women of European ancestry. Ann Intern Med 2009;150:541ŌĆō550. PMID: 19380854.



32. Ripatti S, Tikkanen E, Orho-Melander M, Havulinna AS, Silander K, Sharma A, et al. A multilocus genetic risk score for coronary heart disease: case-control and prospective cohort analyses. Lancet 2010;376:1393ŌĆō1400. PMID: 20971364.



33. Jee SH, Yun JE, Park EJ, Cho ER, Park IS, Sull JW, et al. Body mass index and cancer risk in Korean men and women. Int J Cancer 2008;123:1892ŌĆō1896. PMID: 18651571.


34. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. 1992. 10th Rev. Geneva: World Health Organization.
35. Chambless LE, Diao G. Estimation of time-dependent area under the ROC curve for long-term risk prediction. Stat Med 2006;25:3474ŌĆō3486. PMID: 16220486.


36. Lim TS, Loh WY, Shih YS. A comparison of prediction accuracy, complexity, and training time of thirty-three old and new classification algorithms. Mach Learn 2000;40:203ŌĆō228.

37. Colditz GA, Atwood KA, Emmons K, Monson RR, Willett WC, Trichopoulos D, et al. Risk Index Working Group, Harvard Center for Cancer Prevention. Harvard report on cancer prevention volume 4: Harvard Cancer Risk Index. Cancer Causes Control 2000;11:477ŌĆō488. PMID: 10880030.


38. Cappell MS. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and management of colon cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2008;37:1ŌĆō24. PMID: 18313537.


39. Horne BD, Anderson JL, Carlquist JF, Muhlestein JB, Renlund DG, Bair TL, et al. Generating genetic risk scores from intermediate phenotypes for use in association studies of clinically significant endpoints. Ann Hum Genet 2005;69:176ŌĆō186. PMID: 15720299.



40. Ortlepp JR, Lauscher J, Janssens U, Minkenberg R, Hanrath P, Hoffmann R. Analysis of several hundred genetic polymorphisms may improve assessment of the individual genetic burden for coronary artery disease. Eur J Intern Med 2002;13:485ŌĆō492. PMID: 12446192.


41. Aston CE, Ralph DA, Lalo DP, Manjeshwar S, Gramling BA, DeFreese DC, et al. Oligogenic combinations associated with breast cancer risk in women under 53 years of age. Hum Genet 2005;116:208ŌĆō221. PMID: 15611867.


42. Yang ZR, Chou KC. Bio-support vector machines for computational proteomics. Bioinformatics 2004;20:735ŌĆō741. PMID: 14751989.


43. American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2006. 2006. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society.
44. Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, H├Čhler T, Galle PR, B├╝chler MW. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2005;365:153ŌĆō165. PMID: 15639298.


45. Reeves GK, Travis RC, Green J, Bull D, Tipper S, Baker K, et al. Incidence of breast cancer and its subtypes in relation to individual and multiple low-penetrance genetic susceptibility loci. JAMA 2010;304:426ŌĆō434. PMID: 20664043.


46. Slattery ML, Kerber RA. Family history of cancer and colon cancer risk: the Utah Population Database. J Natl Cancer Inst 1994;86:1618ŌĆō1626. PMID: 7932826.


47. Jasperson KW, Tuohy TM, Neklason DW, Burt RW. Hereditary and familial colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010;138:2044ŌĆō2058. PMID: 20420945.



48. McCashland TM, Brand R, Lyden E, de Garmo P. CORI Research Project. Gender differences in colorectal polyps and tumors. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:882ŌĆō886. PMID: 11280569.


Fig.┬Ā1
Effects of family history of CRC and GRS on the risk of CRC in Koreans who participated in the KCPS-II (adjusted for age, BMI and smoking status) (A) counted GRS in men and women (B) weighted GRS in men and women. CRC, colorectal cancer; GRS, genetic risk scores; KCPS-II, Korean Cancer Prevention Study-II; BMI, body mass index; OR, odds ratio. aMeans statistically significant.
Table┬Ā1.
General characteristics of case participants and control participants in KCPS-II
Table┬Ā2.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for colorectal cancer using counted and weighted genetic risk score in Korean men and women in KCPS-II
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 30 Crossref
- 7,722 View
- 89 Download
- Related articles in GNI





